Generally, XML (Extensible Mark-up Language) is one of the commonly used data exchange formats to interchange the data between servers.
In android, we have a three types of XML parsers to parse the XML data to get the required information in android applications, those are
- DOM Parser
- SAX Parser
- XMLPullParser
Android DOM Parser
In android, DOM Parser will use an object-based approach to create and parse the XML files in android applications.
To know more about parsing XML using DOM Parser in android, check this Android XML Parsing using DOM Parser.
Android SAX Parser
In android, SAX stands for Simple API for XML and SAX is widely used API for XML parsing.
To know more about parsing XML using SAX parser in android, check this Android XML Parsing using SAX Parser.
Now we will see how to use XMLPullParser in android applications to parse the XML data to get the required information.
Android XMLPullParser
In android, XMLPullParser interface provides the functionality to parse the XML files in android applications. The XMLPullParser is simple and efficient way to parse the XML data when compared with DOM Parser and SAX Parser.
The XMLPullParser contains a method called next() to provide an access to high-level parsing events. The next() method will advances the parser to the next event.
Following are the different type of events available in XMLPullParser which will be seen by next() method.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| START_DOCUMENT | The parser will start processing the XML document. |
| START_TAG | In this event we can get the start tag in XML. |
| TEXT | In this event, we can read the Text content by using the getText() method. |
| END_TAG | An end tag was read. |
| END_DOCUMENT | No more events are available. |
Android XMLPullParser XML Parsing
The XMLPullParser will examines an XML file with a series of events, such as START_DOCUMENT, START_TAG, TEXT, END_TAG and END_DOCUMENT to parse the XML document.
To read and parse the XML data using XMLPullParser in android, we need to create an instance of XMLPullParserFactory, XMLPullParser objects in android applications.
Following is the code snippet of reading and parsing the XML data using XMLPullParser in android applications with XMLPullParserFactory, XMLPullParser and series of events to get the required information from XML objects.
XmlPullParser parser = parserFactory.newPullParser();
parser.setFeature(XmlPullParser.FEATURE_PROCESS_NAMESPACES,false);
parser.setInput(istream,null);
String tag = "" , text = "";
int event = parser.getEventType();
while (event!= XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT){
tag = parser.getName();
switch (event){
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
if(tag.equals("user"))
user = new HashMap<>();
break;
case XmlPullParser.TEXT:
text=parser.getText();
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
switch (tag){
case "name": user.put("name",text);
break;
case "designation": user.put("designation",text);
break;
case "location": user.put("location",text);
break;
}
break;
}
event = parser.next();
}
If you observe above code snippet, we used XMLPullParserFactory, XMLPullParser with series of events to get the required information from XML objects.
Now we will see how to parse XML data using XMLPullParser and bind the parsed XML data to Listview in android application with examples.
Android XML Parsing with XMLPullParser Example
Following is the example of parsing the XML data and get the required information from it using XMLPullParser in android applications.
Create a new android application using android studio and give names as XMLParserExample. In case if you are not aware of creating an app in android studio check this article Android Hello World App.
Once we are done with the creation of an application, create an assets folder under /src/main folder and add a new resource file (userdetails.xml), for that right click on assets folder à add new Android resource file à Give name as userdetails.xml like as shown below.
Now open userdetails.xml file and write the code like as shown below.
userdetails.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<users>
<user>
<name>Suresh Dasari</name>
<designation>Team Leader</designation>
<loation>Hyderabad</loation>
</user>
<user>
<name>Rohini Alavala</name>
<designation>Agricultural Officer</designation>
<loation>Guntur</loation>
</user>
<user>
<name>Trishika Dasari</name>
<designation>Charted Accountant</designation>
<loation>Guntur</loation>
</user>
</users>
Now open activity_main.xml file from \res\layout folder path and write the code like as shown below.
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/user_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:dividerHeight="1dp" />
</LinearLayout>
After that create an another layout file (list_row.xml) in /res/layout folder to show the data in listview, for that right click on layout folder à add new Layout resource file à Give name as list_row.xml and write the code like as shown below.
list_row.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="5dip" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textSize="17dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/designation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/name"
android:layout_marginTop="7dp"
android:textColor="#343434"
android:textSize="14dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/location"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/designation"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/designation"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:textColor="#343434"
android:textSize="14dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
Now open your main activity file MainActivity.java from \java\com.tutlane.xmlparserexample path and write the code like as shown below
MainActivity.java
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserException;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
try{
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> userList = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<String,String> user = new HashMap<>();
ListView lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.user_list);
InputStream istream = getAssets().open("userdetails.xml");
XmlPullParserFactory parserFactory = XmlPullParserFactory.newInstance();
XmlPullParser parser = parserFactory.newPullParser();
parser.setFeature(XmlPullParser.FEATURE_PROCESS_NAMESPACES,false);
parser.setInput(istream,null);
String tag = "" , text = "";
int event = parser.getEventType();
while (event!= XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT){
tag = parser.getName();
switch (event){
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
if(tag.equals("user"))
user = new HashMap<>();
break;
case XmlPullParser.TEXT:
text=parser.getText();
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
switch (tag){
case "name": user.put("name",text);
break;
case "designation": user.put("designation",text);
break;
case "location": user.put("location",text);
break;
case "user":
if(user!=null)
userList.add(user);
break;
}
break;
}
event = parser.next();
}
ListAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, userList, R.layout.list_row,new String[]{"name","designation","location"}, new int[]{R.id.name, R.id.designation, R.id.location});
lv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
If you observe above code, we used XMLPullParserFactory, XMLPullParser with series of events to get the required information from XML files.
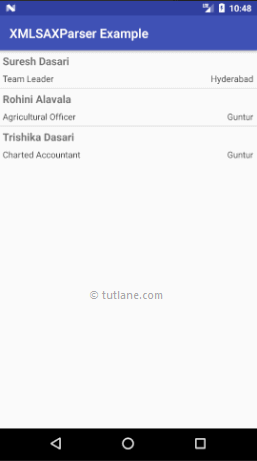
Output of Android XML Parsing with XMLPullParser Example
When we run the above program in the android studio we will get the result as shown below.
This is how we can parse the XML data using XMLPullParser in android applications to get the required information.